Transgenic Animals Definition Biology
By DAMARIS BENNY DANIEL II Msc.
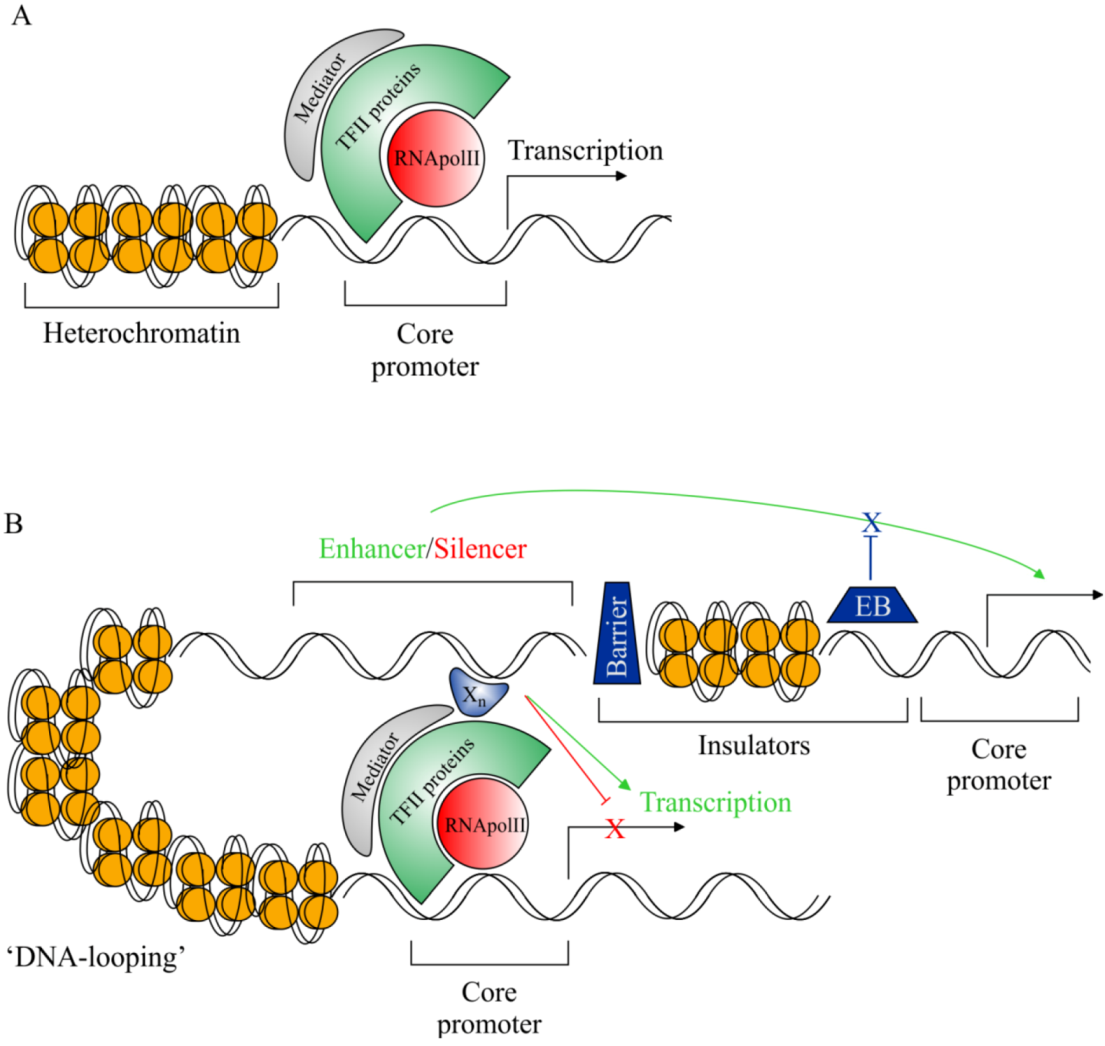
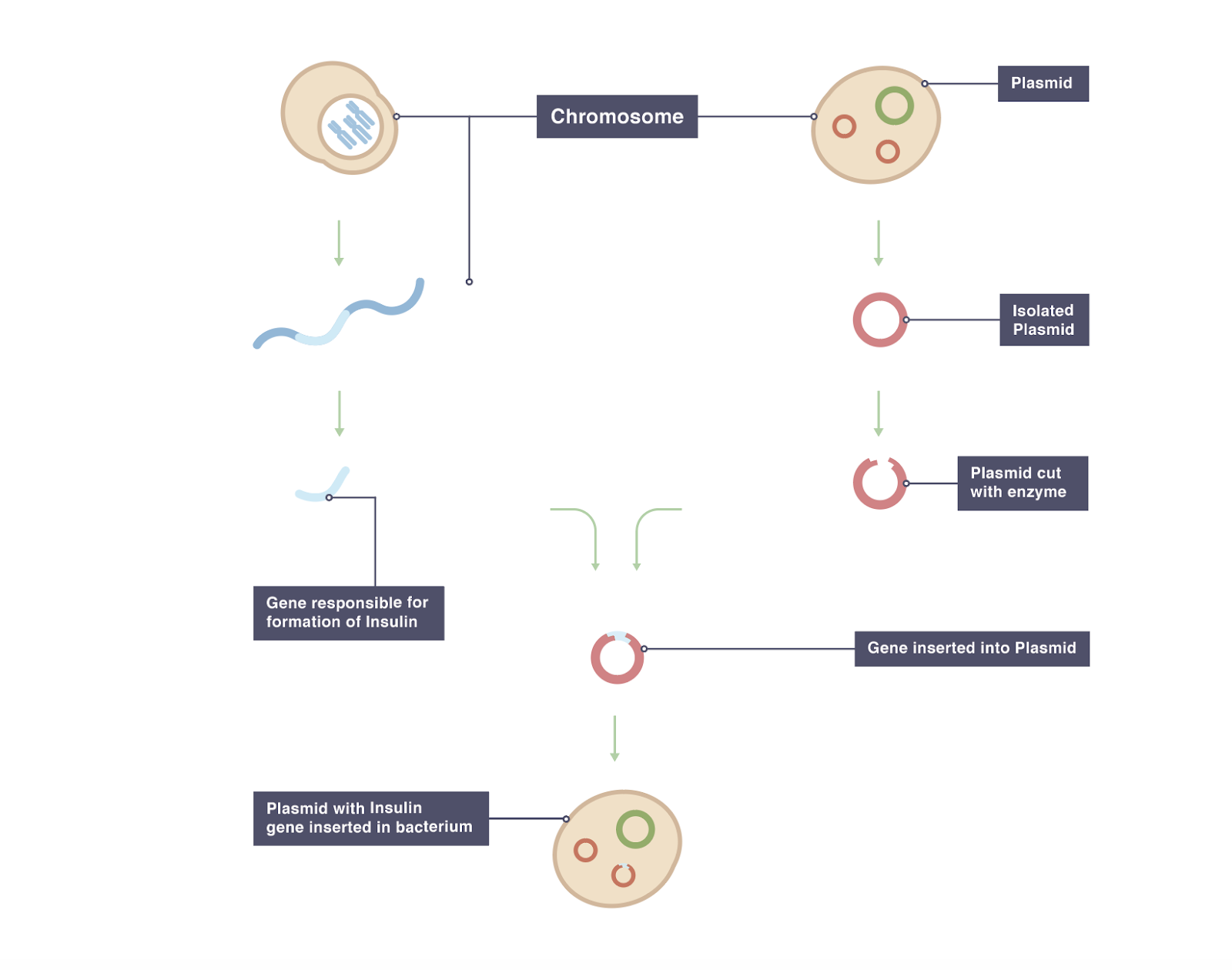
Transgenic animals definition biology. A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been altered by the transfer of a gene or genes from another species or breed. Recombinant DNA methodology is used to construct the gene that is intended to express desirable qualities during the growth and development of the recipient animal. In addition to the gene.
Sheep goats pigs cows rabbits rats mice fish insects parasites and even humans have previously been used in this modification process. Transgenic animals are specially designed to study the role of genes in the development of certain diseases. Transgenic Animals Definition Biology.
Transgenic plants can be made by introducing foreign DNA into a variety of different tissues. The animal which carry foreign genes are called transgenic animals. They are then exposed to the toxic substances and the effects studied.
Transgenic animals definition biology. Transgenics describes the process of introducing foreign deoxyribonucleic acid DNA into a host organisms genome. Transgenic animal industrial applications 3 chemical safety testing toxicity-sensitive transgenic animals animal bioreactor protein production.
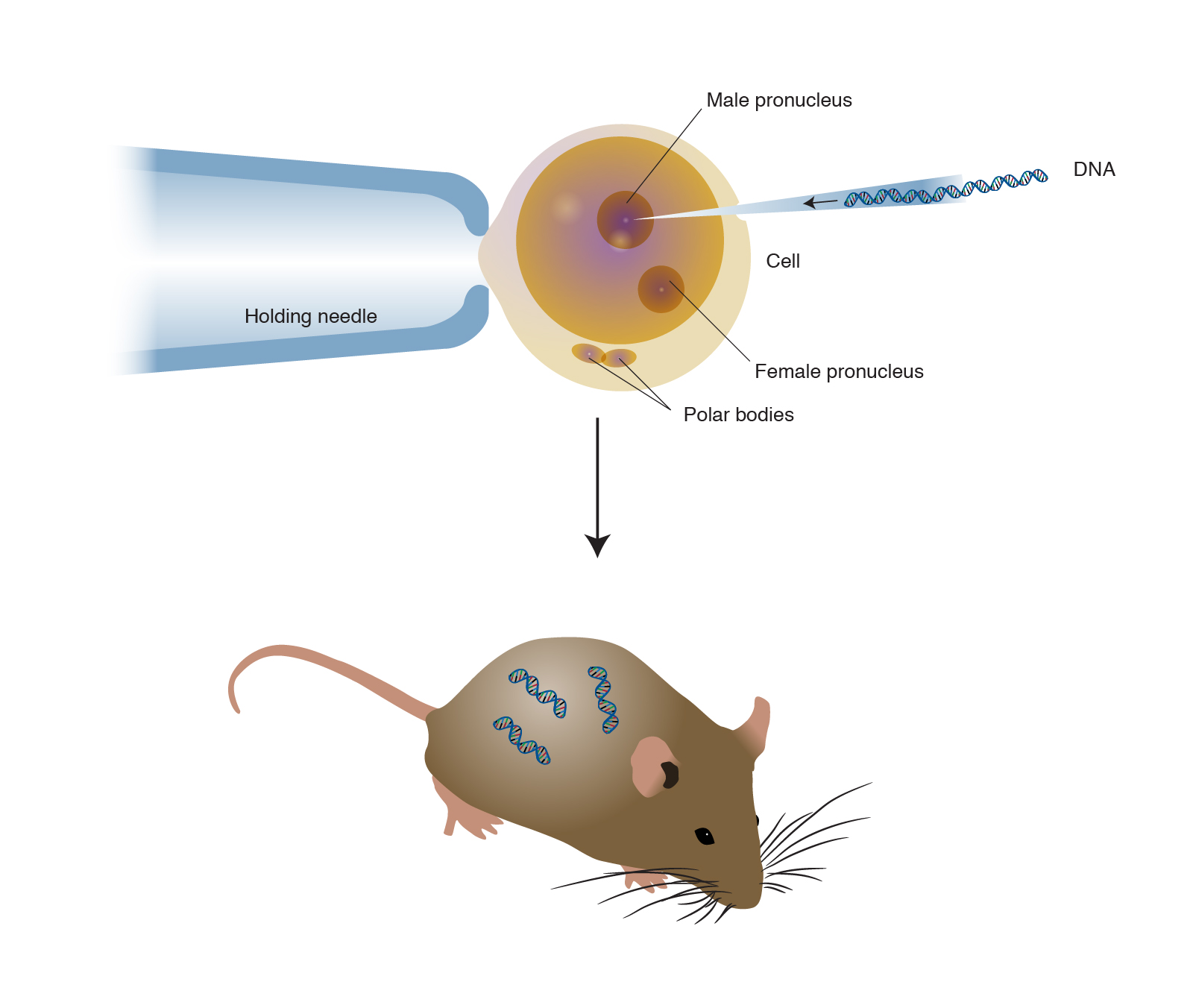
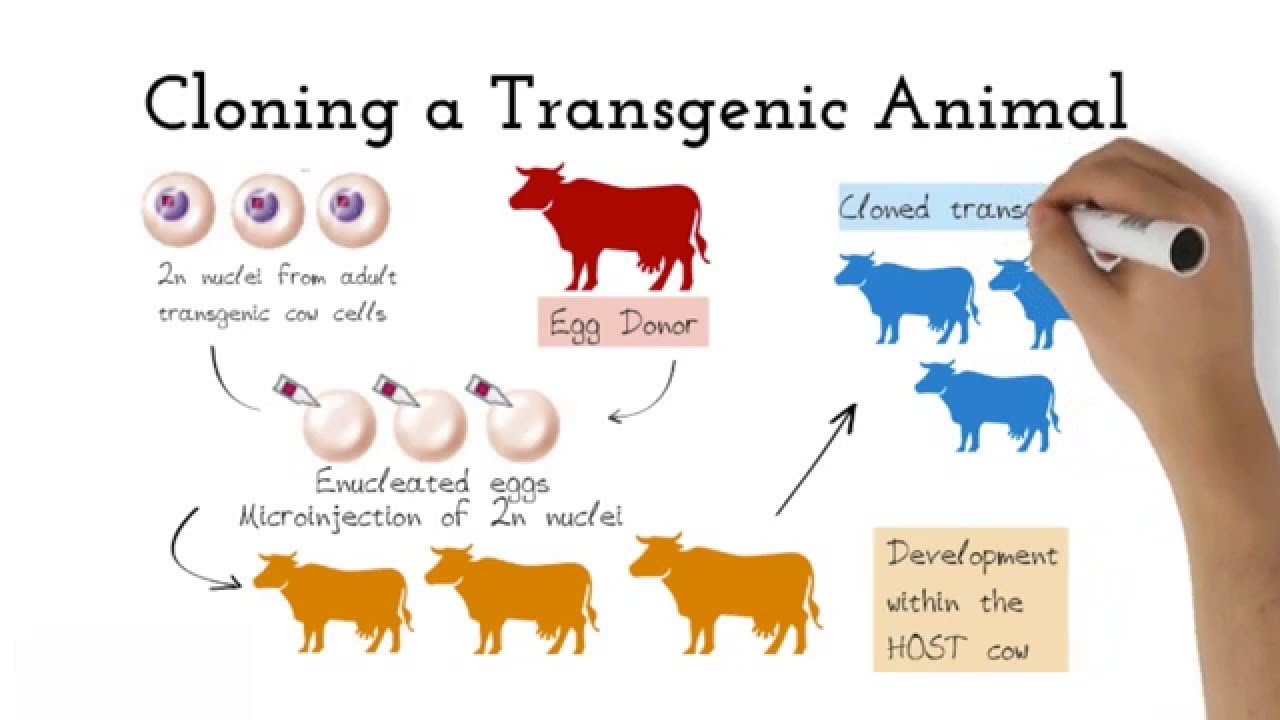
The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology. Disease Animal Models - BSRC Alexander FlemingTransgenic Animal Models - Biomedcode. Animals transgenic animals or the offspring of such animals into which cloned genetic material has been experimentally transferred by microinjection of foreign dna either directly or into embryos or differentiated cell types.
Moreover in order to devise a cure for these diseases the transgenic animals are used as model organisms. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology. Full article A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been changed to carry genes from other species.

_1602913203_391831-5.jpg)