Food Chain Definition Biology

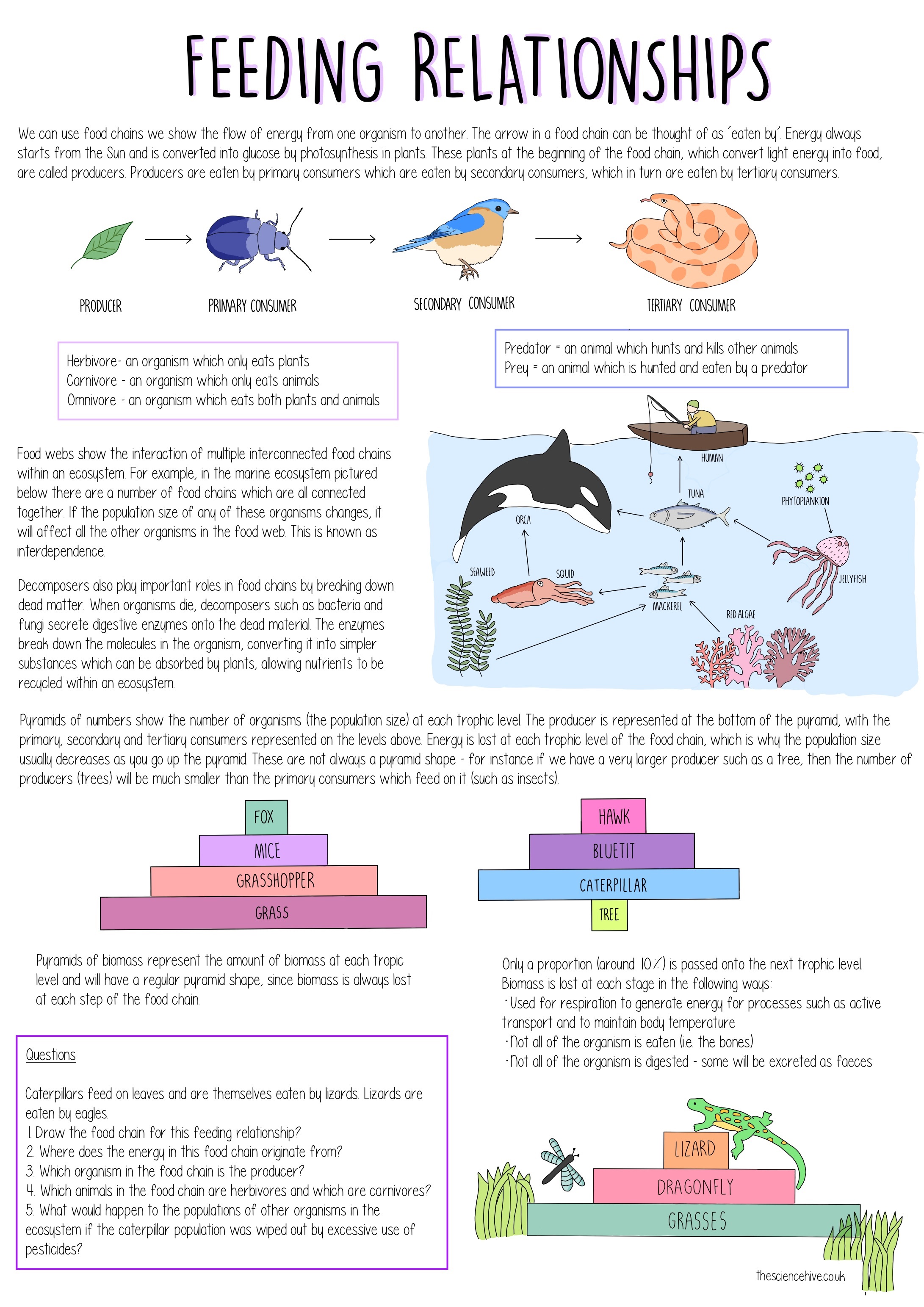
The consumers include all the other types of organisms in the ecosystem like herbivores carnivores etc.
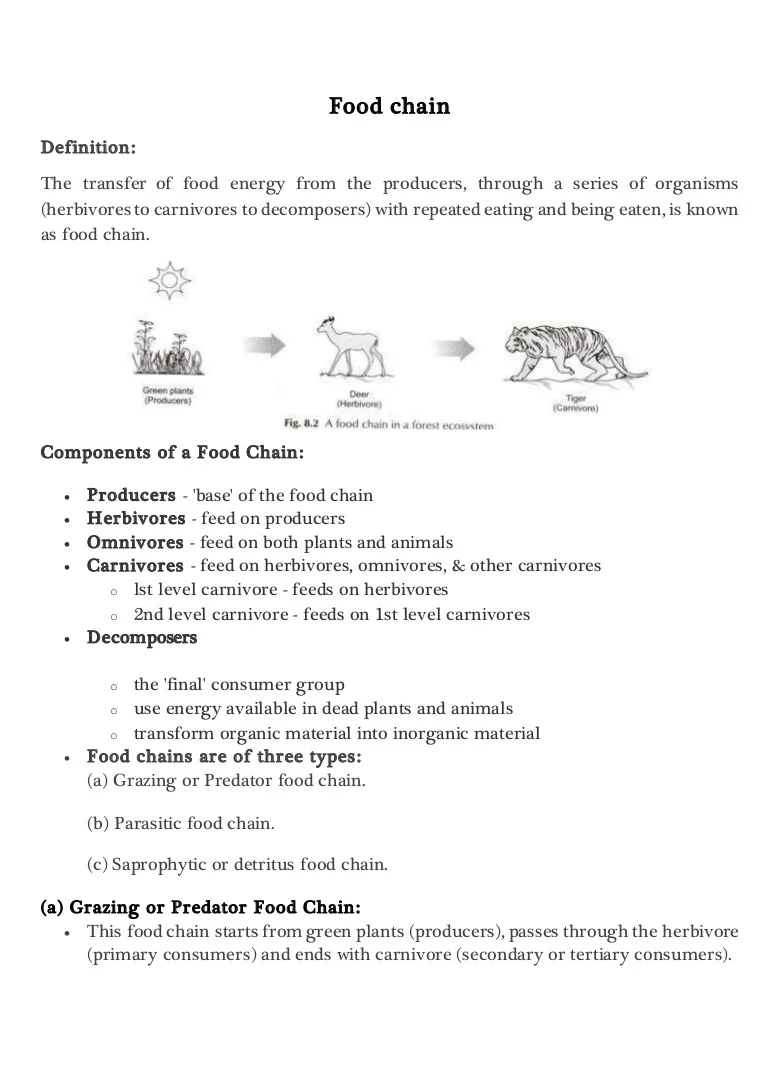
Food chain definition biology. A food chain outlines who eats whom. A food chain is basically made up of producers and consumers. A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms such as grass or trees which use radiation from the sun to make their food and ending at apex predator species like grizzly bears or killer whales detritivores like earthworms or woodlice or decomposer species such as fungi or bacteria.
For example if you had a hamburger for lunch you might be part of a food chain. Shows what eats what in a particular habitat. The producers are represented primarily by the green plants and to a lesser extent by the photosynthetic bacteria.
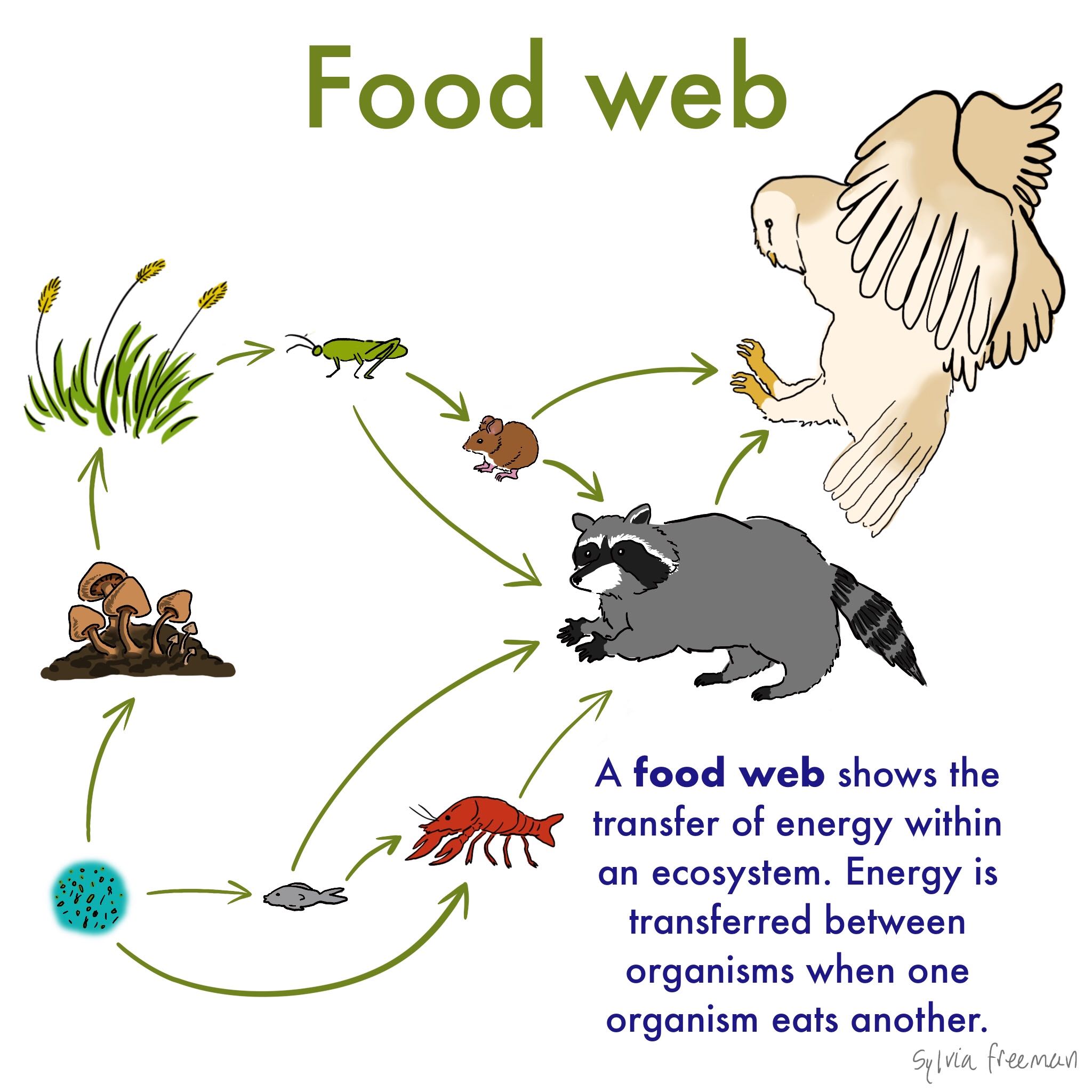
The trophic chain food chain or food chain is known as the mechanism by which organic matter nutrients and energy are transferred by the different types of living things that make up a biological community or ecosystem. A sequence usually shown as a diagram of feeding relationships between organisms showing who eats what and the movement of energy through trophic levels. The arrows used to link each organism to the next represent the direction of energy flow.
See more Encyclopedia articles on. Food Chain Definition 6. Detritus food chain is the type of food chain that starts with dead organic materials.
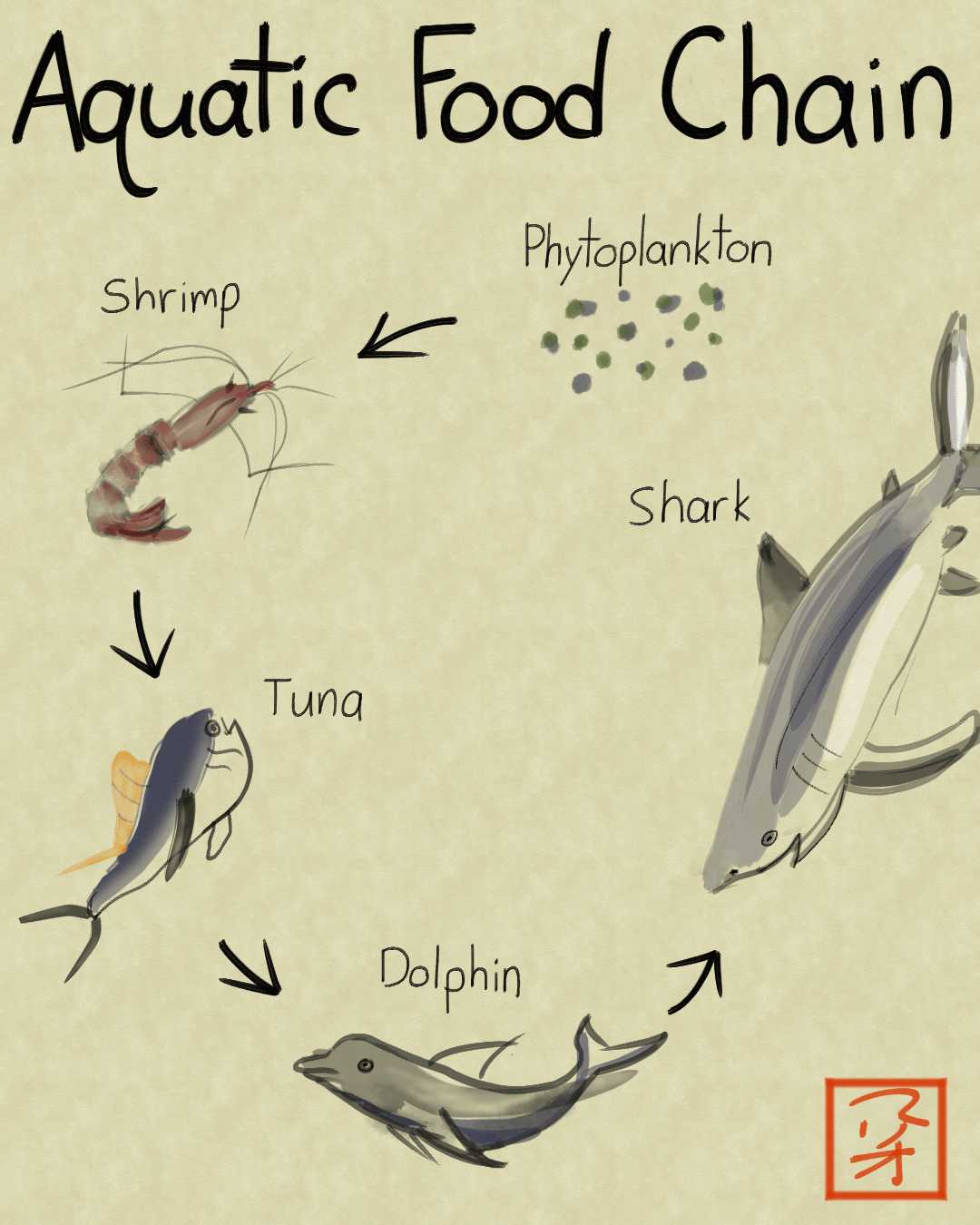
It shows the flow of energy and materials from one organism to the next beginning with a producer. Food chain is a chart showing the flow of energy food from one organism to the next beginning with a producer. It begins with producer organism follows the chain and ends with decomposer organism.
Producers who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. Food chain - ecology a community of organisms where each member is eaten in turn by another member. Environmental Studies ADVERTISEMENT.