Cell Membrane Structure And Function Ppt

The Plasma membrane is a thin bi- layered structure which surrounds each cell consists of lipids phospholipids 75 cholesterol 20glycolipids 5 proteins partially or completely embedded carbohydrates etc 6-10 nm thick.
Cell membrane structure and function ppt. Thin barrier separating inside of cell cytoplasm from outside environment Function. Cell wall Great wall of China Chloroplast Site of photosynthesis Vacuole large central takes up most part of cell Cell membrane Regulates substances in and out of the cell. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics results in mucoid coating of lungs and.
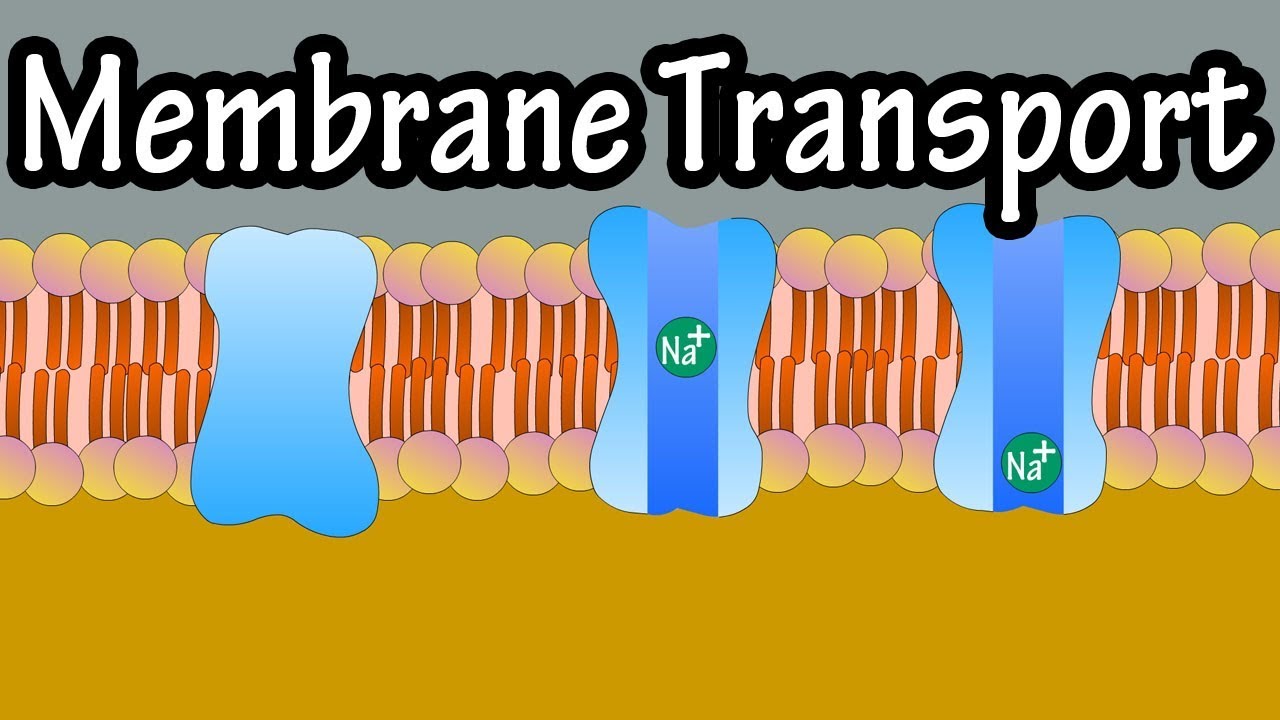
W O R K T O G E T H E R Recap Cell parts such as cell membranes are made up of biological molecules. Functions of the Plasma Membrane selectively isolates the cells contents from the external environment regulates the exchange of essential substances between the cells contents and the external environment allows communication with other cells gives strength shape and protection to the cell. Functions of Membrane Proteins Can be peripheral or integral Ion channels allow flow of ions in and out of cell Carriers selectively move POLAR substances across membrane transporters Receptors specific to various molecules Ligand substance that binds to receptor Linkers help anchor cells together by bonding proteins or filaments together Cell-Identity Markers.
The structure and function of cellular organelles the cell is the smallest unit of life. Likewise the cell membrane is a thin flexible layer that seals the inside of. That of the extracellular fluid.
Membranes also exist within cells forming various. Fluid pliableeasily moved - due to lipid component -phospholipids can move laterally b. JacksonChapter 7Membrane Structure andFunction Lectures by Erin Barley Kathleen Fitzpatrick 2011 Pearson Education Inc.
Outer membrane that encloses the cell contents. Mosaic made of a combination of molecules lipids proteins and carbs Cell Membrane Animation Phospholipids Fatty acid. Vesicles may combine with plasma membrane to secrete contents Lysosomes Contain digestive enzymes Functions Aid in cell renewal Break down old cell parts Digests invaders Vacuoles Membrane bound storage sacs More common in plants than animals Contents Water Food wastes Mitochondria Break down fuel molecules cellular respiration Glucose Fatty acids Release energy ATP.
It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cells shape. Membrane Design fluid-mosaic model a. The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane as a flexible boundary of a cell.